
Engineers must be able to maneuver the spacecraft to take its most vulnerable areas out of the path of the meteoroid stream. On Earth, these debris fields are associated with meteor showers. The shower environment describes the threat of meteoroid streams associated with comets passing through Earth’s orbit. Engineers must determine what area of the spacecraft is most vulnerable to sporadic meteoroids, and prepare stronger shielding mechanisms. The sporadic environment describes the threat of meteoroids created by asteroids or comets.

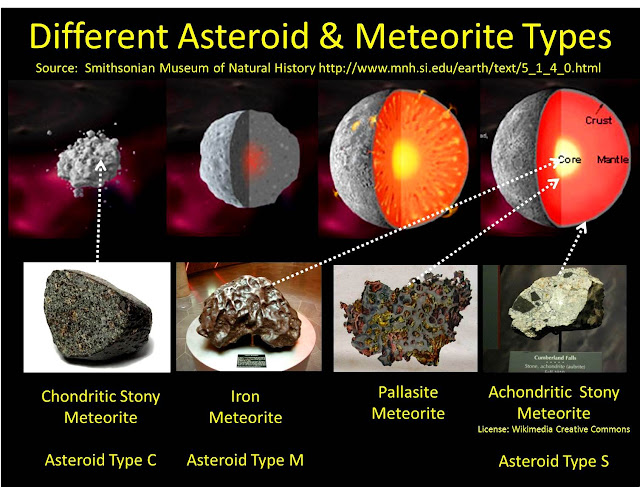
To do this, they have classified three different “meteoroid environments”: the sporadic environment, the shower environment, and the lunar environment. Engineers must prepare and equip spacecraft to avoid or withstand meteoroid impacts. This could endanger astronauts, result in the loss of valuable scientific instruments, and cost millions of dollars. Spacecraft The impact of even a micrometeoroid can damage the windows, thermal protection systems, and pressurized containers of spacecraft. Space agencies such as NASA do monitor the movement of meteoroids, however, for two reasons: potential impact with spacecraft and potential impact with Earth. Assessing the Impact Meteoroids are generally as harmless as any other celestial body-they’re specks of dust floating around the sun. Iron and nickel-iron meteoroids are massive and dense, while stony meteoroids are lighter and more fragile. Most meteoroids are made of silicon and oxygen ( minerals called silicates) and heavier metals like nickel and iron. Meteoroids crash into these bodies, creating craters and throwing space dust (more meteoroids) back into the solar system. Meteoroid impacts are probably the largest contributor to “ space weathering.” Space weathering describes the processes that act upon a celestial body that doesn’t have an airy atmosphere, such as asteroids, many moons, or the planets Mars and Mercury. A very small percentage of meteoroids are rocky pieces that break off from the Moon and Mars after celestial bodies-often asteroids or other meteoroids- impact their surfaces. Meteoroids shed by a comet usually orbit together in a formation called a meteoroid stream. The dusty tail may contain hundreds or even thousands of meteoroids and micrometeoroids. As a comet approaches the sun, the “dirty snowball” of the comet’s nucleus sheds gas and dust. Other meteoroids are the debris that comets shed as they travel through space. This can put the meteoroids on a collision course with a planet or moon. The force of the asteroid collision can throw the meteoroid debris-and sometimes the asteroids themselves-out of their regular orbit. As asteroids smash into each other, they produce crumbly debris-meteoroids. Many meteoroids are formed from the collision of asteroids, which orbit the sun between the paths of Mars and Jupiter in a region called the asteroid belt. The fastest meteoroids travel through the solar system at a speed of around 42 kilometers (26 miles) per second.

Different meteoroids travel around the sun at different speeds and in different orbits. Meteoroids are even found on the edge of the solar system, in regions called the Kuiper belt and the Oort cloud. They orbit the sun among the rocky inner planets, as well as the gas giants that make up the outer planets.
Meteoroids, especially the tiny particles called micrometeoroids, are extremely common throughout the solar system. Meteoroids are lumps of rock or iron that orbit the sun, just as planets, asteroids, and comets do.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
